(Note that finding a Hamiltonian cycle is an NP-hard problem and there is much research going on to find theoretical results about finding not only necessary but also sufficient criteria for a graph to be Hamiltonian. The following theorem is one such research[^1591] result in providing a necessary and sufficient criterion for a planar graph to be Hamiltonian. The theorem is also the main motivation for defining the concept of minimal tree decomposability \(\tau(G)\) of a graph \(G\).)
For all simple planar connected graphs \(G\), the following equivalence holds: \(G\) is Hamiltonian, if and only if the minimal tree decomposability of every of its dual graphs equals \(2\), formally:
\[\text{Simple and planar }G:~G\text{ is Hamiltonian}\quad\Longleftrightarrow\quad \tau(G^*)=2\text{ for all dual graphs }G^*\text{ of }G.\]
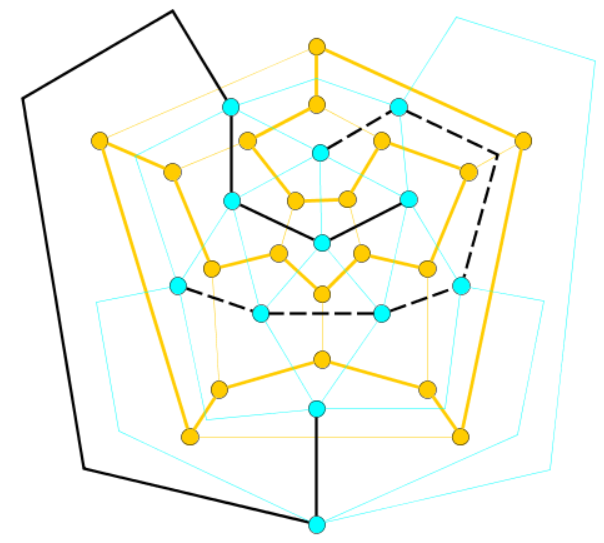
The idea for this equivalence is illustrated in the following example:
* The planar graph is drawn using the orange color (here a dodecahedron graph).
* The bold orange lines mark a Hamiltonian circle.
* The blue graph is the dual (here an icosahedron graph).
* The bold black lines mark the decomposition of the icosahedron graph into two tree graphs (marked solid and dotted).
* The theorem states for this example that the dodecahedron graph is Hamiltonian if and only if the minimum decomposition of its dual icosahedron graph leads to exactly two trees (but not more and not less than two trees).
* The constructive nature of the proof makes use of the fact that a Hamiltonian cycle of a planar graph (if it is Hamiltonian) can be constructed from the edges dual to exactly those edges of the dual graph, which are not part of the decomposition trees (in the example below those are the thin blue edges crossing the bold orange edges), or by removing the edges crossed by the dual edges of the decomposition trees (in the example below those are the thin orange edges crossed by the bold black edges).
new:branchcorollary:The 4-colors Problem and Planar Hamiltonian Graphs
Let $G$ be a simple planar which is also Hamiltonian. Then it can be colored in
Proofs: 1