◀ ▲ ▶Branches / Topology / Proposition: p-Norm, Taxicab Norm, Euclidean Norm, Maximum Norm
Proposition: p-Norm, Taxicab Norm, Euclidean Norm, Maximum Norm
A generalization of the Euclidean Norm is defined by the p-norm. Let $p$ be a real number $\ge 1$. Let $x=(x_1,x_2,\ldots x_n)$ be a vector of a vector space \(V\) over the field of real numbers \(\mathbb R\) or the field of complex numbers \(\mathbb C\).
The p-norm of $x$ is defined by
$$||x||_p:=\left(\sum_{\nu=1}^n|x_\nu|^p\right)^{1/p}.$$
Special Cases
- $p=1$: taxicab norm $$||x||_1:=\sum_{\nu=1}^n|x_\nu|.$$
- $p=2$: Euclidean Norm $$||x||_2:=\sqrt{\sum_{\nu=1}^n|x_\nu|^2}.$$
- $p=3$: 3-Norm $$||x||_3:=\sqrt[ 3 ]{\sum_{\nu=1}^n|x_\nu|^3}.$$
- ...
- $p\to\infty$: maximum norm $$||x||_\infty:=\max_{\nu} |x_\nu|.$$
The p-norm can be visualized for two dimensional vectors $x=(x_1,x_2)$ as follows: The below figure shows some unity circles (i.e. the values of coordinates $(x_1,x_2)$, for which the p-norm $||x||_p$ takes the value $1$):
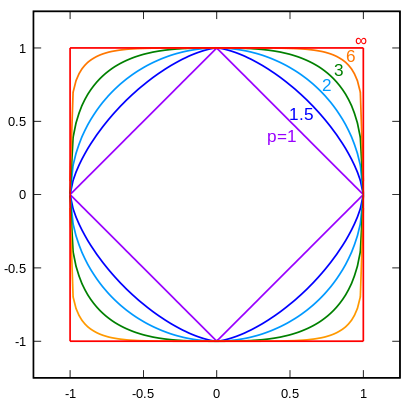
From Wikimedia by Quartl
Table of Contents
Proofs: 1
- Proposition: Maximum Norm as a Limit of p-Norms
Mentioned in:
Proofs: 1 2 3 4
Propositions: 5 6 7
Thank you to the contributors under CC BY-SA 4.0! 

- Github:
-

References
Bibliography
- Forster Otto: "Analysis 1, Differential- und Integralrechnung einer Veränderlichen", Vieweg Studium, 1983
