(related to Problem: The Great Monad)
The areas of circles are to each other as the squares of their diameters. If you have a circle $2$ in. in diameter and another $4$ in. in diameter, then one circle will be four times as great in area as the other, because the square of $4$ is four times as great as the square of $2.$ Now, if we refer to Diagram $1,$ we see how two equal squares may be cut into four pieces that will form one larger square; from which it is self-evident that any square has just half the area of the square of its diagonal. In Diagram $2$ I have introduced a square as it often occurs in ancient drawings of the Monad; which was my reason for believing that the symbol had mathematical meanings, since it will be found to demonstrate the fact that the area of the outer ring or annulus is exactly equal to the area of the inner circle. Compare Diagram $2$ with Diagram $1,$ and you will see that as the square of the diameter $CD$ is double the square of the diameter of the inner circle or $CE,$ therefore, the area of the larger circle is double the area of the smaller one, and consequently the area of the annulus is exactly equal to that of the inner circle. This answers our first question.
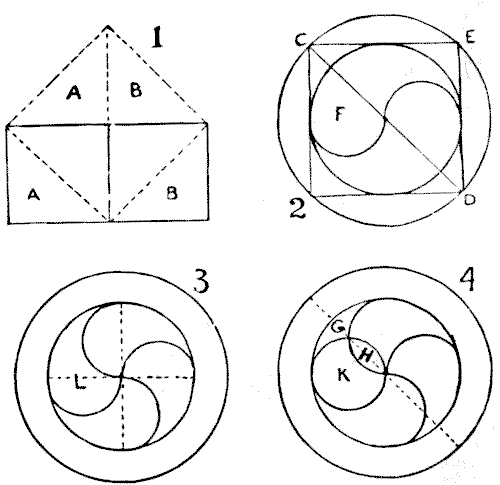
In Diagram $3$ I show the simple solution to the second question. It is obviously correct, and may be proved by the cutting and superposition of parts. The dotted lines will also serve to make it evident. The third question is solved by the cut $CD$ in Diagram $2,$ but it remains to be proved that the piece $F$ is really one-half of the Yin or the Yan. This we will do in Diagram $4.$ The circle $K$ has one-quarter the area of the circle containing Yin and Yan, because its diameter is just one-half the length. Also $L$ in Diagram $3$ is, we know, one-quarter the area. It is, therefore, evident that $G$ is exactly equal to $H,$ and therefore half $G$ is equal to half $H.$ So that what $F$ loses from $L$ it gains from $K,$ and $F$ must be half of Yin or Yan.
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this edition or online at http://www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.