Many pastimes of great antiquity, such as chess, have so developed and changed down the centuries that their original inventors would scarcely recognize them. This is not the case with Tangrams, a recreation that appears to be at least four thousand years old, that has apparently never been dormant, and that has not been altered or "improved upon" since the legendary Chinaman Tan first cut out the seven pieces shown in Diagram I. If you mark the point $B,$ midway between $A$ and $C,$ on one side of a square of any size, and $D,$ midway between $C$ and $E,$ on an adjoining side, the direction of the cuts is too obvious to need further explanation. Every design in this article is built up from the seven pieces of blackened cardboard. It will at once be understood that the possible combinations are infinite.
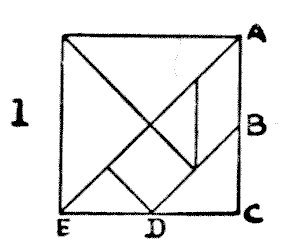
The late Mr. Sam Loyd, of New York, who published a small book of very ingenious designs, possessed the manuscripts of the late Mr. Challenor, who made a long and close study of Tangrams. This gentleman, it is said, records that there were originally seven books of Tangrams, compiled in China two thousand years before the Christian era. These books are so rare that, after forty years' residence in the country, he only succeeded in seeing perfect copies of the first and seventh volumes with fragments of the second. Portions of one of the books, printed in gold leaf upon parchment, were found in Peking by an English soldier and sold for three hundred pounds.
A few years ago a little book came into my possession, from the library of the late Lewis Carroll, entitled The Fashionable Chinese Puzzle. It contains three hundred and twenty-three Tangram designs, mostly nondescript geometrical figures, to be constructed from the seven pieces. It was "Published by J. and E. Wallis, 42 Skinner Street, and J. Wallis, Jun., Marine Library, Sidmouth" (South Devon). There is no date, but the following note fixes the time of publication pretty closely: "This ingenious contrivance has for some time past been the favourite amusement of the ex-Emperor Napoleon, who, being now in a debilitated state and living very retired, passes many hours a day in thus exercising his patience and ingenuity." The reader will find, as did the great exile, that much amusement, not wholly uninstructive, may be derived from forming the designs of others. He will find many of the illustrations to this article quite easy to build up, and some rather difficult. Every picture may thus be regarded as a puzzle.
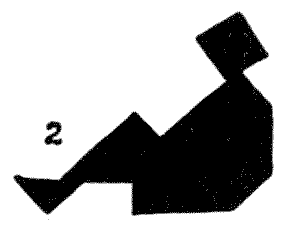
But it is another pastime altogether to create new and original designs of a pictorial character, and it is surprising what extraordinary scope the Tangrams afford for producing pictures of real life—angular and often grotesque, it is true, but full of character. I give an example of a recumbent figure (2) that is particularly graceful, and only needs some slight reduction of its angularities to produce an entirely satisfactory outline.
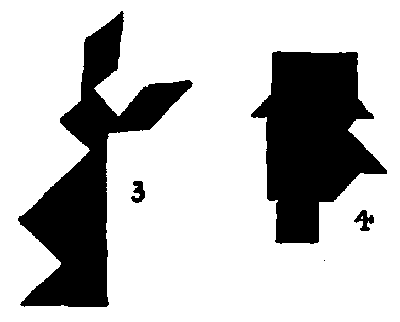
As I have referred to the author of Alice in Wonderland, I give also my designs of the March Hare (3) and the Hatter (4). I also give an attempt at Napoleon (5), and a very excellent Red Indian with his Squaw by Mr. Loyd (6 and 7). A large number of other designs will be found in an article by me in The Strand Magazine for November 1908.

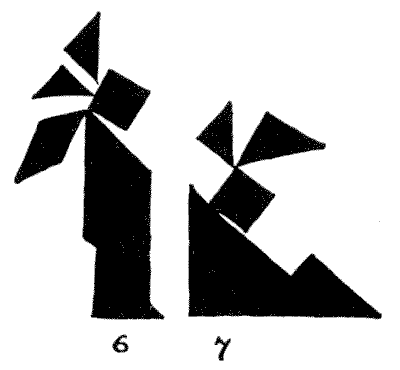
On the appearance of this magazine article, the late Sir James Murray, the eminent philologist, tried, with that amazing industry that characterized all his work, to trace the word "tangram" to its source. At length he wrote as follows:—"One of my sons is a professor in the Anglo-Chinese college at Tientsin. Through him, his colleagues, and his students, I was able to make inquiries as to the alleged Tan among Chinese scholars. Our Chinese professor here (Oxford) also took an interest in the matter and obtained information from the secretary of the Chinese Legation in London, who is a very eminent representative of the Chinese literati."
"The result has been to show that the man Tan, the god Tan, and the 'Book of Tan' are entirely unknown to Chinese literature, history, or tradition. By most of the learned men the name, or allegation of the existence, of these had never been heard of. The puzzle is, of course, well known. It is called in Chinese ch'i ch'iao t'u; literally, 'seven-ingenious-plan' or 'ingenious-puzzle figure of seven pieces.' No name approaching 'tangram,' or even 'tan,' occurs in Chinese, and the only suggestions for the latter were the Chinese t'an, 'to extend'; or t'ang, Cantonese dialect for 'Chinese.' It was suggested that probably some American or Englishman who knew a little Chinese or Cantonese, wanting a name for the puzzle, might concoct one out of one of these words and the European ending 'gram.' I should say the name 'tangram' was probably invented by an American some little time before 1864 and after 1847, but I cannot find it in print before the 1864 edition of Webster. I have therefore had to deal very shortly with the word in the dictionary, telling what it is applied to and what conjectures or guesses have been made at the name, and giving a few quotations, one from your own article, which has enabled me to make more of the subject than I could otherwise have done."
Several correspondents have informed me that they possess, or had possessed, specimens of the old Chinese books. An American gentleman writes to me as follows:—"I have in my possession a book made of tissue paper, printed in black (with a Chinese inscription on the front page), containing over three hundred designs, which belongs to the box of 'tangrams,' which I also own. The blocks are seven in number, made of mother-of-pearl, highly polished and finely engraved on either side. These are contained in a rosewood box $2 \frac 18$ in. square. My great uncle, ——, was one of the first missionaries to visit China. This box and book, along with quite a collection of other relics, were sent to my grandfather and descended to myself."

My correspondent kindly supplied me with rubbings of the Tangrams, from which it is clear that they are cut in the exact proportions that I have indicated. I reproduce the Chinese inscription (8) for this reason. The owner of the book informs me that he has submitted it to a number of Chinamen in the United States and offered as much as a dollar for a translation. But they all steadfastly refused to read the words, offering the lame excuse that the inscription is Japanese. Natives of Japan, however, insist that it is Chinese. Is there something occult and esoteric about Tangrams, that it is so difficult to lift the veil? Perhaps this page will come under the eye of some reader acquainted with the Chinese language, who will supply the required translation, which may, or may not, throw a little light on this curious question.
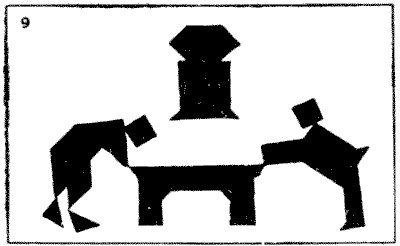
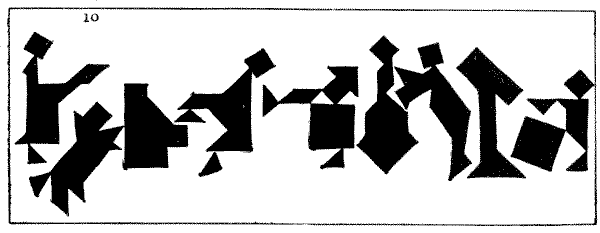
By using several sets of Tangrams at the same time we may construct more ambitious pictures. I was advised by a friend not to send my picture, "A Game of Billiards" (9), to the Academy. He assured me that it would not be accepted because the "judges are so hide-bound by convention." Perhaps he was right, and it will be more appreciated by Post-impressionists and Cubists. The players are considering a very delicate stroke at the top of the table. Of course, the two men, the table, and the clock are formed from four sets of Tangrams. My second picture is named "The Orchestra" (10), and it was designed for the decoration of a large hall of music. Here we have the conductor, the pianist, the fat little cornet-player, the left-handed player of the double-bass, whose attitude is life-like, though he does stand at an unusual distance from his instrument, and the drummer-boy, with his imposing music-stand. The dog at the back of the pianoforte is not howling: he is an appreciative listener.

One remarkable thing about these Tangram pictures is that they suggest to the imagination such a lot that is not really there. Who, for example, can look for a few minutes at Lady Belinda (11) and the Dutch girl (12) without soon feeling the haughty expression in the one case and the arch look in the other? Then look again at the stork (13), and see how it is suggested to the mind that the leg is actually much more slender than any one of the pieces employed. It is really an optical illusion. Again, notice in the case of the yacht (14) how, by leaving that little angular point at the top, a complete mast is suggested. If you place your Tangrams together on white paper so that they do not quite touch one another, in some cases the effect is improved by the white lines; in other cases, it is almost destroyed.
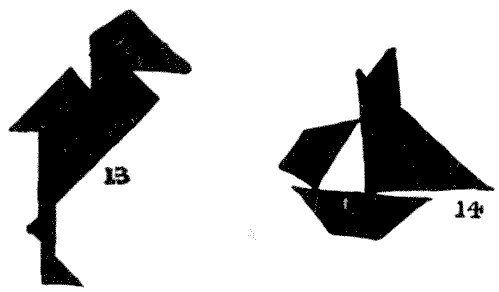
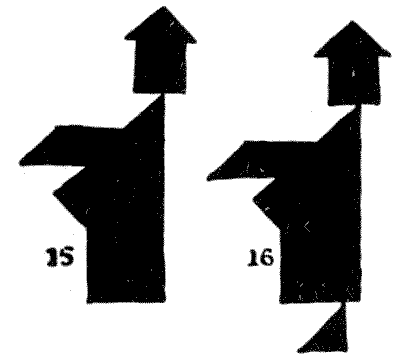
Finally, I give an example from the many curious paradoxes that one happens upon in manipulating Tangrams. I show designs of two dignified individuals (15 and 16) who appear to be exactly alike, except for the fact that one has a foot and the other has not. Now, both of these figures are made from the same seven Tangrams. Where does the second man get his foot from?
Solutions: 1
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this edition or online at http://www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.