In right-angled triangles, the square on the side subtending the right angle is equal to the (sum of the) squares on the sides containing the right angle.
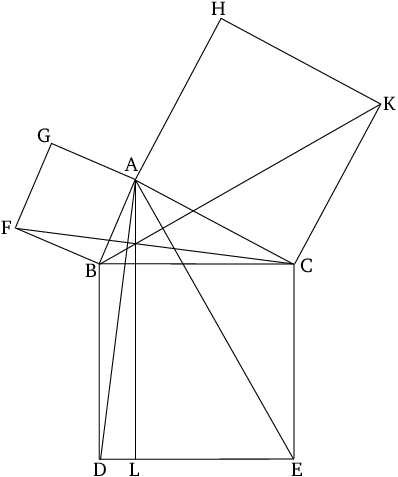
In a right triangle (\(\triangle{ABC}\)), the square on the hypotenuse (\(\overline{BC}\)) is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides (\(\overline{AB}\), \(\overline{CA}\)).
This theorem is also known as the theorem of Pythagoras.
Proofs: 1
Parts: 1
Persons: 2
Proofs: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
Propositions: 32 33 34
Sections: 35
Topics: 36 37