(related to Chapter: Finite Automata (Finite Sequential Machines))
$\epsilon$-NFA can be illustrated using diagrams like it was the case for the DFA and the NFA.
Please note that the $\epsilon$-NFA are more general than NFA. Their definition include NFA as a special case. Of course, also the DFA are included as a special case.
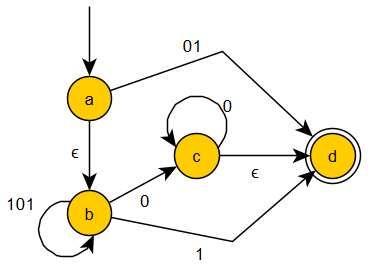
The following example of an $\epsilon$-NFA accepts all strings over the alphabet $\{0,1\}$ with the following structure $$L=\{101\}^*\{0\}\{0\}^*\cup\{101\}^*\{1\}\cup \{01\}$$
The following example of an $\epsilon$-NFA accepts all strings over the alphabet $\{1,2,3\}$ with the following structure $$L=\{1^i2^j3^k\mid i,j,k\in\mathbb N\}$$
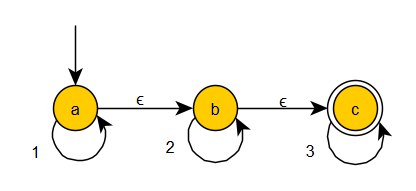
The empty word $\epsilon$ will be accepted, although $a$ is not one of the final states.
Applications: 1